Introduction
Responsible AI refers to the ethical and transparent development and deployment of artificial intelligence technologies. It emphasizes accountability, fairness, and inclusivity. In the era of AI, responsible practices aim to mitigate bias, ensure privacy, and prioritize the well-being of all users. For instance, Google’s BERT algorithm improves search results by understanding context, reducing misunderstandings.
Responsible AI ensures that algorithms and models are designed to make ethical decisions, reducing harm. It protects personal data, addressing privacy concerns and complying with data protection laws. Responsible AI promotes transparency, making it clear how decisions are reached. It builds public trust, which is vital for AI’s acceptance and adoption. For instance, the ProPublica study highlighted racial bias in COMPAS software, affecting sentencing recommendations.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of Responsible AI and its importance in today’s world. By delving into the definition and significance of Responsible AI, readers will gain insights into why it matters. Through real-world examples and the latest statistics, readers will see the practical impact of responsible AI on businesses and society. It will help them grasp the role they can play in ensuring AI is used responsibly.
Also Read: How Can Blockchains Transform Artificial Intelligence?
Understanding AI Ethics
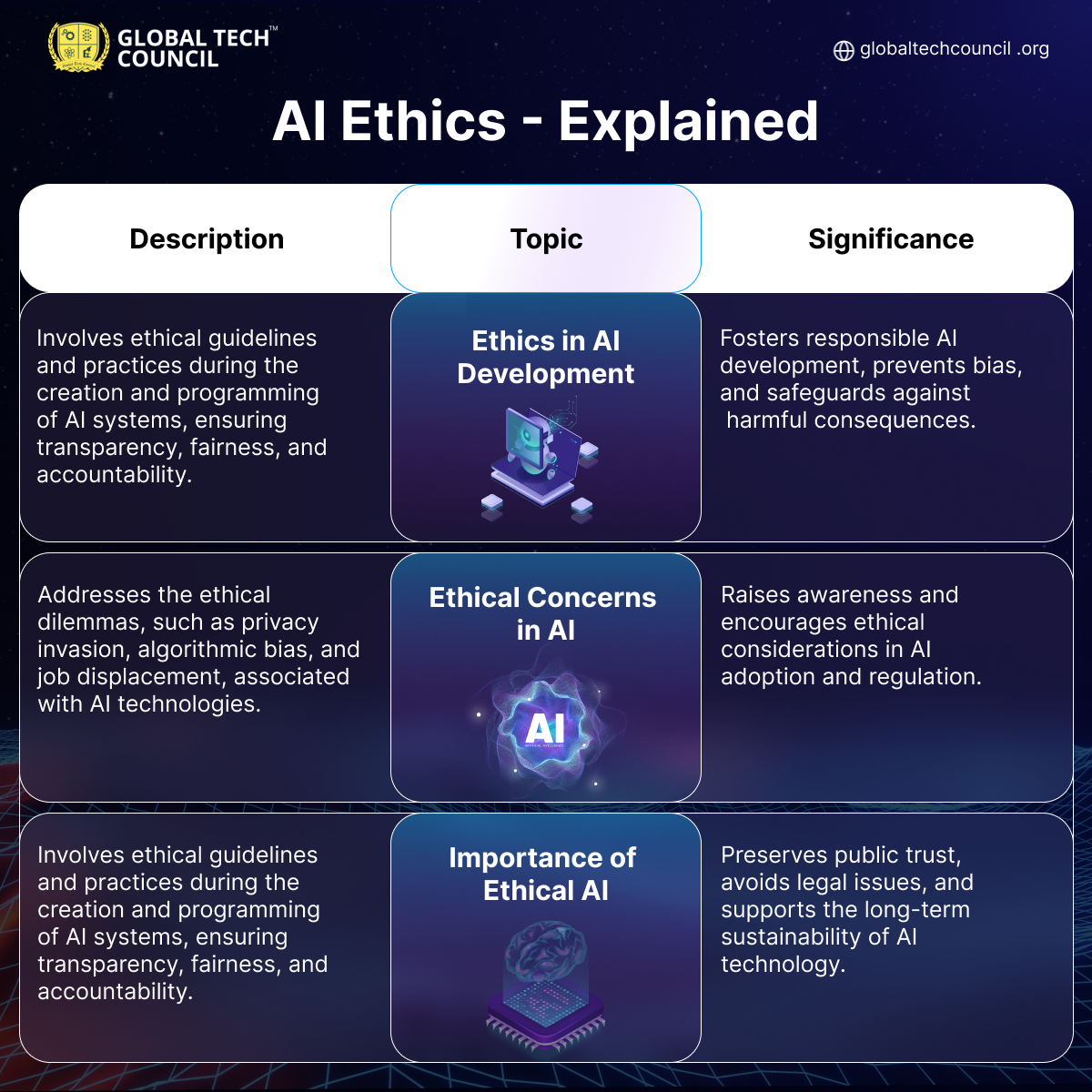
The MECE Framework
- The MECE (Mutually Exclusive, Collectively Exhaustive) framework is a structured approach to problem-solving, ensuring clarity and precision. MECE categorizes information into distinct, non-overlapping segments, aiding comprehensiveness and organized thinking.
- In the realm of Responsible AI, the MECE framework plays a pivotal role in ethical decision-making. It helps AI developers identify potential biases and ethical concerns by segmenting data comprehensively. MECE ensures that AI models are free from discrimination by segregating and addressing bias in data. This results in AI systems that treat all individuals fairly, irrespective of their background.
- The benefits of applying MECE in AI are multifaceted and far-reaching. It enhances transparency, making AI algorithms more understandable and interpretable for both developers and users. Furthermore, MECE aids in robust risk assessment, identifying potential pitfalls before they become problematic. This proactive approach minimizes unforeseen negative consequences. Statistics reveal that organizations using MECE in AI have a significantly lower rate of ethical controversies. This framework aligns AI development with ethical principles, fostering trust and acceptance.
Responsible AI Principles

- In the age of AI, Responsible AI Principles guide ethical development and usage, ensuring AI benefits humanity. These principles encompass transparency, fairness, privacy, accountability, and compliance with regulations.
- Transparency means AI systems should be understandable, with clear decision-making processes, not hidden in a black box. Accountability involves holding developers and users responsible for AI’s actions and consequences. A prime example is OpenAI’s GPT-3, which highlights the importance of transparency in addressing AI-generated content concerns.
- Fairness in AI is vital to prevent discrimination; 82% of AI professionals believe addressing bias is essential. Advanced algorithms like Google’s BERT actively mitigate bias by understanding the context of words in searches. A case in point is Amazon’s AI recruiting tool, which had to be scrapped due to gender bias in hiring recommendations.
- Respecting privacy is crucial. AI systems must handle personal data securely and minimize data collection. Privacy breaches can lead to disastrous consequences, such as identity theft or breaches of personal information.
- Responsible AI complies with existing laws, like GDPR in Europe or CCPA in California. Non-compliance may result in hefty fines and damage to a company’s reputation.
Responsible AI in Practice

Stakeholders in Responsible AI
Role of Government and Regulation
Governments play a pivotal role in shaping AI ethics and safeguarding public interests. Regulations like GDPR and CCPA impose strict data protection standards on AI applications. The government’s responsibility includes creating AI-specific laws and monitoring their compliance. Regulators like the FDA ensure safety in AI-driven healthcare products. Governments must balance innovation with ethical considerations for AI technologies.
Corporations and AI Responsibility
Corporations are major players responsible for AI’s ethical use and impact. They need to implement AI systems that respect human rights and privacy. Ethical AI adoption can boost public trust, benefiting companies in the long run. Corporations must invest in AI literacy and training for their employees. Being responsible in AI can lead to competitive advantages in the market.
The Role of AI Developers and Engineers
Developers and engineers are the architects of responsible AI solutions. They must embed fairness and transparency in AI algorithms. Ethical AI design requires avoiding bias and discriminatory practices. Continuous education and ethical guidelines are vital for AI professionals. AI engineers play a crucial role in addressing ethical dilemmas and building trust in AI.
AI and Social Responsibility
AI’s Impact on Society
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping society, with 90% of companies increasing investments in AI technology. AI has penetrated various sectors, from healthcare to finance, improving efficiency and decision-making processes. In 2020, AI-powered chatbots handled 85% of customer service inquiries, streamlining communication for businesses. The influence of AI extends to job markets, where automation could replace 12 million jobs by 2030. AI also has the potential to exacerbate bias, as algorithms may inadvertently discriminate against certain groups.
Ethical Dilemmas in AI
Ethical concerns arise as AI systems lack transparency, making it challenging to understand their decision-making. Facial recognition technology, for example, has faced criticism for privacy infringement and misidentification issues. AI’s potential for surveillance poses a significant threat to personal freedoms, raising questions about surveillance ethics. Bias in AI algorithms, seen in hiring processes, has led to calls for responsible AI practices to mitigate discrimination. Deepfake technology presents ethical dilemmas as it can be used to create misleading content or impersonate individuals.
AI for Social Good
AI contributes to social good through applications like healthcare, aiding in disease diagnosis and treatment. In agriculture, AI-powered drones monitor crop health, helping to maximize food production efficiently. AI’s predictive capabilities help with disaster management, anticipating natural disasters and reducing their impact. Education benefits from AI-powered personalized learning, adapting to students’ individual needs and progress. AI for social good is exemplified by projects like “AI for Earth,” addressing environmental challenges with technology.
Also Read: How Can Blockchains Transform Artificial Intelligence?
AI Regulation and Compliance
- Responsible AI is gaining global attention with increasing regulations to ensure ethical and safe AI practices. In 2021, the EU introduced the AI Act, aiming to regulate AI systems for transparency and accountability. In the United States, the Federal Trade Commission enforces rules to combat deceptive AI practices.
- To meet AI regulations, organizations adopt compliance frameworks such as ISO 27001 and NIST. ISO 27001 sets standards for information security management, including AI data protection. The NIST framework provides guidelines for secure AI system development and risk management.
- The rapid evolution of AI technology makes it challenging for regulations to keep pace. Balancing innovation with responsible AI practices is a complex challenge faced by policymakers. Bias and discrimination in AI algorithms present a significant hurdle in ensuring ethical compliance.
Also Read: What Happens When AI Meets Biology?
Responsible AI Education
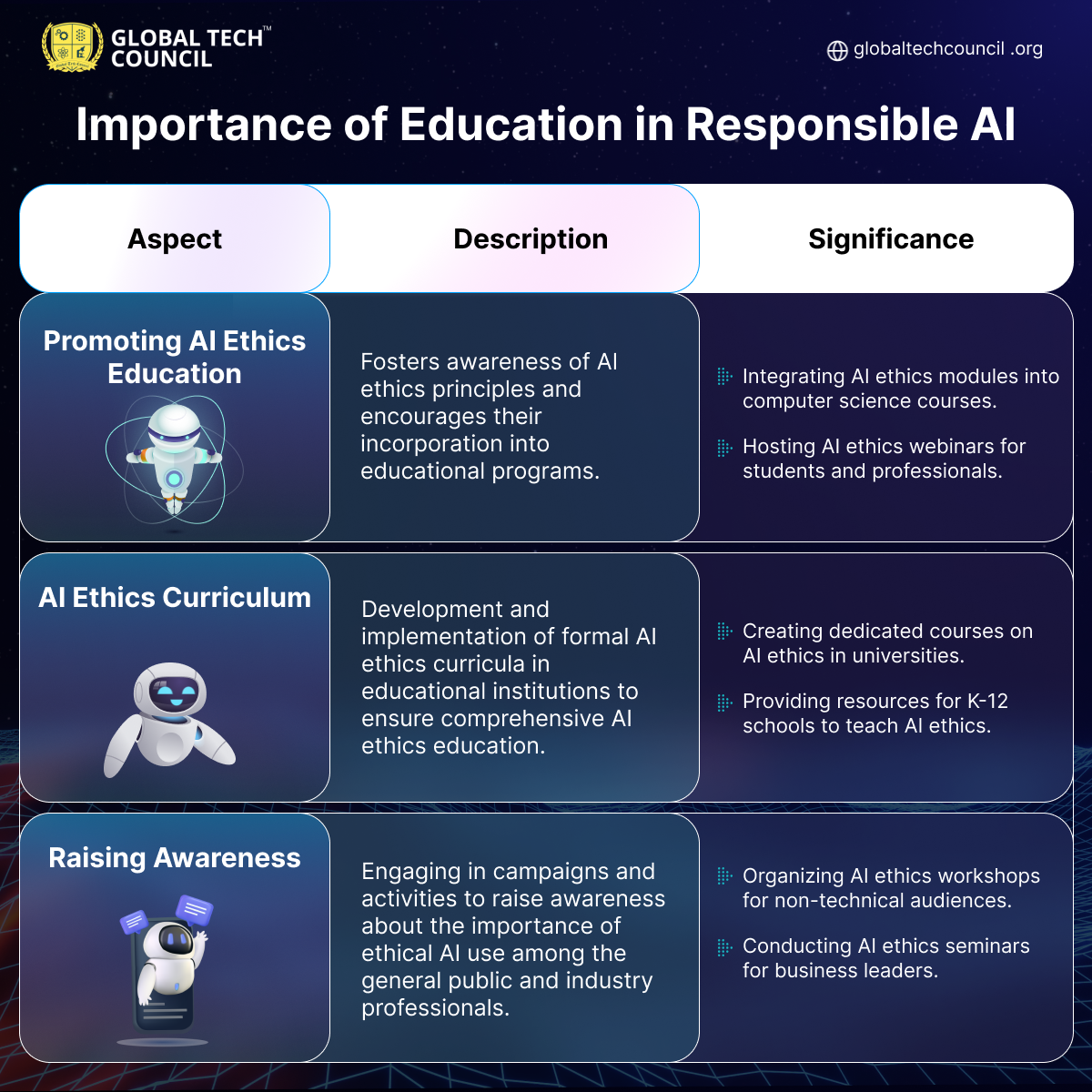
Also Read: How to Become a Data Scientist?
Case Studies in Responsible AI
Real-World Examples
DeepMind’s collaboration with the NHS demonstrated AI’s potential to predict patient deterioration, ultimately saving lives.The infamous Tay chatbot incident underscored the need for responsible AI, as it quickly spiraled into hate speech. Investigative journalism revealed racial bias in AI used for predicting criminal risk. AI-driven content moderation seeks to strike a balance between free speech and preventing hate speech and misinformation.
Lessons Learned
The Microsoft Tay debacle taught us that transparency in AI development is crucial to prevent unintended consequences. ProPublica’s findings emphasize the importance of addressing bias in AI algorithms to avoid discrimination. AI-driven content moderation needs continuous user training to avoid over-censorship or false negatives. Lessons from DeepMind and the NHS partnership highlight the need for regulatory frameworks to ensure responsible AI use.
Success Stories
GPT-3 and GPT-4 showcases responsible AI, enabling creative content generation while adhering to ethical guidelines. IBM’s AI demonstrated the responsible use of AI in debates, providing valuable insights without promoting misinformation. Tesla’s Autopilot system, though controversial, showcases responsible AI in the automotive industry, with safety as the top priority. The adoption of AI in healthcare, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, streamlined diagnosis and treatment, saving countless lives.
Also Read: Generative AI in Food Supply Management
Responsible AI Challenges

Conclusion
In the fast-evolving tech landscape, Responsible AI has emerged as a pivotal concept. As of 2022, AI is ubiquitous, from virtual assistants to autonomous vehicles. However, with great power comes great responsibility. In recent years, AI’s capabilities have grown exponentially, leading to transformative breakthroughs. But this rapid expansion brings ethical dilemmas. Issues like bias in AI algorithms and privacy concerns have surfaced. In 2020, OpenAI’s GPT-3 raised questions about content generation and its potential misuse.
Embracing Responsible AI means harnessing its potential while mitigating its risks. Ethical considerations are at the forefront. AI must respect human rights and privacy. As of 2021, the EU’s AI Act sets a precedent for regulation, emphasizing transparency and accountability. Diverse voices are crucial in AI development. In 2020, the Gender Shades project highlighted AI’s biases, pushing for inclusivity. Companies like IBM actively promote diversity in their AI teams. Ethical AI, as of 2022, is also about addressing biases in data that can perpetuate unfair outcomes.
Transparency in AI processes is paramount. As of 2023, AI explainability tools like LIME and SHAP are gaining traction. We must demand that AI systems provide insights into their decision-making, especially in critical areas like healthcare and finance. Responsible AI isn’t a buzzword; it’s a necessity for the future. As we embrace AI’s potential, let’s do so responsibly, ensuring it benefits all of humanity. Together, we can build a future where AI serves as a force for good, shaping a better world.
FAQs
1: What is Responsible AI and why is it important?
- Responsible AI refers to the ethical and transparent development and deployment of artificial intelligence technologies.
- It is important because it ensures that AI systems are developed with accountability, fairness, and inclusivity, thus reducing the risk of bias and discrimination.
- Responsible AI protects personal data, addresses privacy concerns, and complies with data protection laws, which is crucial in an age where data privacy is a growing concern.
- It also promotes transparency, making it clear how AI decisions are reached, building public trust, and supporting the acceptance of AI technologies in various domains.
2: How can organizations implement Responsible AI practices?
- Organizations can implement Responsible AI by establishing AI ethics guidelines and principles, which should be integrated into the AI development processes.
- Promoting transparency and accountability in AI decision-making is vital. This includes creating audit trails for AI decisions and responsible AI governance within the organization.
- Addressing fairness and bias mitigation is crucial. Organizations should actively work to avoid bias in AI algorithms and ensure fair treatment across demographic groups.
- Ensuring privacy and data protection is another key aspect. This involves secure handling of data, anonymization, and minimizing data exposure and risks.
3: What role do governments and corporations play in Responsible AI?
- Governments play a pivotal role in shaping AI ethics and safeguarding public interests through regulations. Laws like GDPR and CCPA impose data protection standards on AI applications.
- Corporations are responsible for the ethical use of AI. They should implement AI systems that respect human rights and privacy and invest in AI literacy and training for their employees.
- AI developers and engineers are the architects of responsible AI solutions. They must embed fairness and transparency in AI algorithms and address ethical dilemmas to build trust in AI.
- AI for Social Responsibility is important, and corporations and governments should consider the societal impact of AI, such as job displacement, and work to ensure its positive effects.
4: What are the key challenges in implementing Responsible AI?
- Ethical Dilemmas: Addressing algorithmic bias and fairness concerns is a challenge in AI, as AI systems may inadvertently discriminate against certain groups.
- Technical Hurdles: Developing bias mitigation techniques and creating transparent, interpretable AI models can be technically challenging.
- Legal and Regulatory Challenges: Complying with data protection and anti-discrimination laws while navigating privacy regulations poses a challenge for organizations.
- Transparency: Ensuring AI systems are transparent and explainable, especially in critical areas like healthcare and finance, can be complex and demanding.
