
Core Focus and Goals
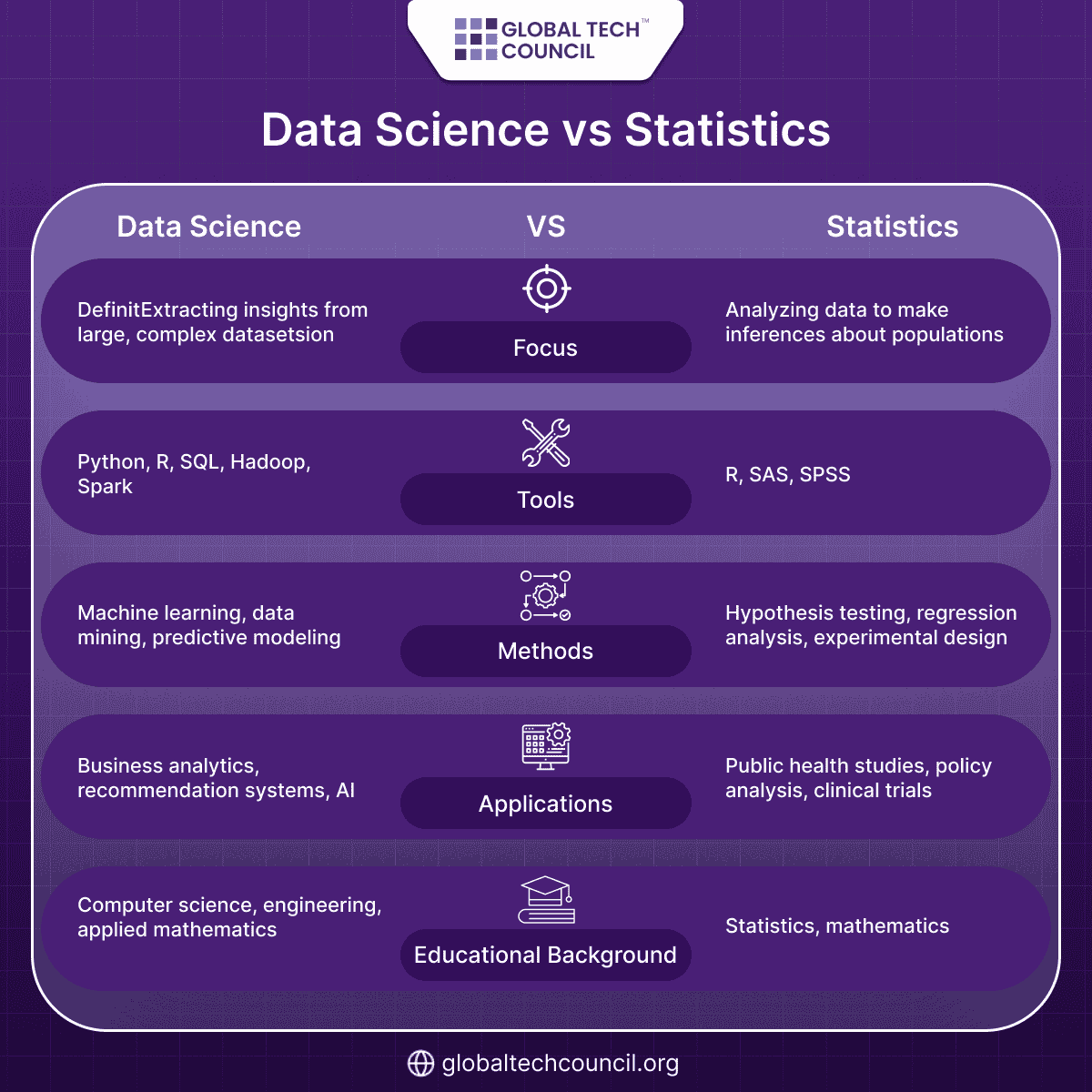
Statistics is a mathematical discipline that focuses on collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting data. It emphasizes understanding relationships between variables and making inferences about populations based on sample data.
Data science is an interdisciplinary field that combines statistics, computer science, and domain knowledge to extract insights from structured and unstructured data. It often involves building predictive models, developing algorithms, and leveraging machine learning to solve complex problems.
Educational Background and Skill Sets
Statisticians typically have a strong foundation in mathematics and statistical theory. They are proficient in statistical software such as R, SAS, or SPSS and focus on hypothesis testing, regression analysis, and experimental design.
Data scientists, while also knowledgeable in statistics, require additional skills in programming, data engineering, and machine learning. They work with big data technologies like Hadoop and Spark, and use programming languages such as Python and SQL to manipulate and analyze data.
Tools and Technologies
Statisticians often use specialized statistical software for their analyses. These tools are designed for rigorous statistical testing and are widely used in academia and research settings.
Data scientists utilize a broader range of tools, including programming languages and big data platforms. These technologies enable them to handle large datasets, perform complex analyses, and deploy machine learning models.
Applications and Industries
Statisticians are commonly employed in government agencies, healthcare, and academia, where they design studies, analyze survey data, and contribute to policy development. For example, they might assess the effectiveness of a new drug or analyze census data to inform public policy.
Data scientists are prevalent in industries like technology, finance, and e-commerce. They develop recommendation systems, detect fraudulent transactions, and optimize supply chains. For instance, a data scientist at a streaming service might analyze user behavior to recommend new content.
Data Science vs Statistics
Career Roles and Responsibilities of Data Scientists and Statisticians
Choosing the Right Path
If you’re interested in building predictive models, working with large datasets, and developing data-driven solutions in a business context, a career in data science may be suitable. Pursuing a Data Science Certification can provide the necessary skills and credentials.
Alternatively, if you prefer a focus on mathematical theory, designing experiments, and making inferences from data, a career in statistics might be the right choice. For those looking to expand their expertise in emerging technologies, consider exploring resources and certifications available at the Blockchain Council.
Conclusion
While data science and statistics share common goals in analyzing data to extract insights, they differ in their approaches, tools, and applications. Understanding these differences can help you choose the career path that aligns with your interests and strengths.

Leave a Reply