
- IoT, or the Internet of Things, is a network of interconnected devices that collect and share data over the internet.
- Businesses use IoT devices like sensors and cameras to monitor, control, and exchange data for improved efficiency and informed decision-making.
- IoT is crucial for staying competitive in modern business, providing real-time data and transforming industries like manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and agriculture.
- The guide aims to help businesses understand and effectively harness IoT potential for enhanced processes, innovation, and new revenue streams.
- IoT comprises interconnected devices, sensors, and systems that collect real-time data, which is processed and analyzed for valuable insights using cloud platforms, advanced analytics, and AI.
- Various communication methods, including wired and wireless protocols, are used in IoT, with security protocols ensuring data protection.
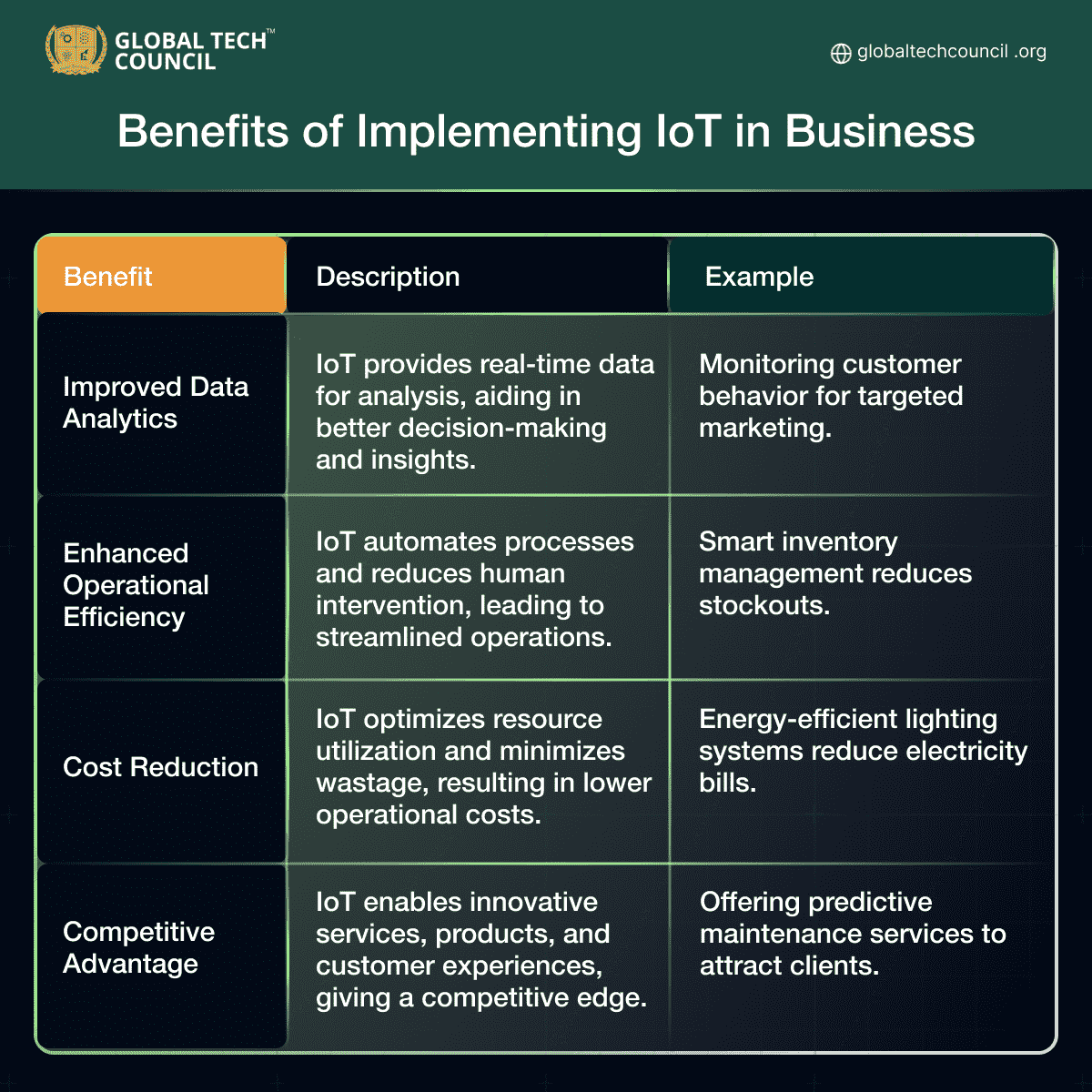
- IoT utilizes sensors like temperature, motion, and RFID tags to revolutionize industries with benefits such as improved data analytics, operational efficiency, cost reduction, and a competitive advantage.
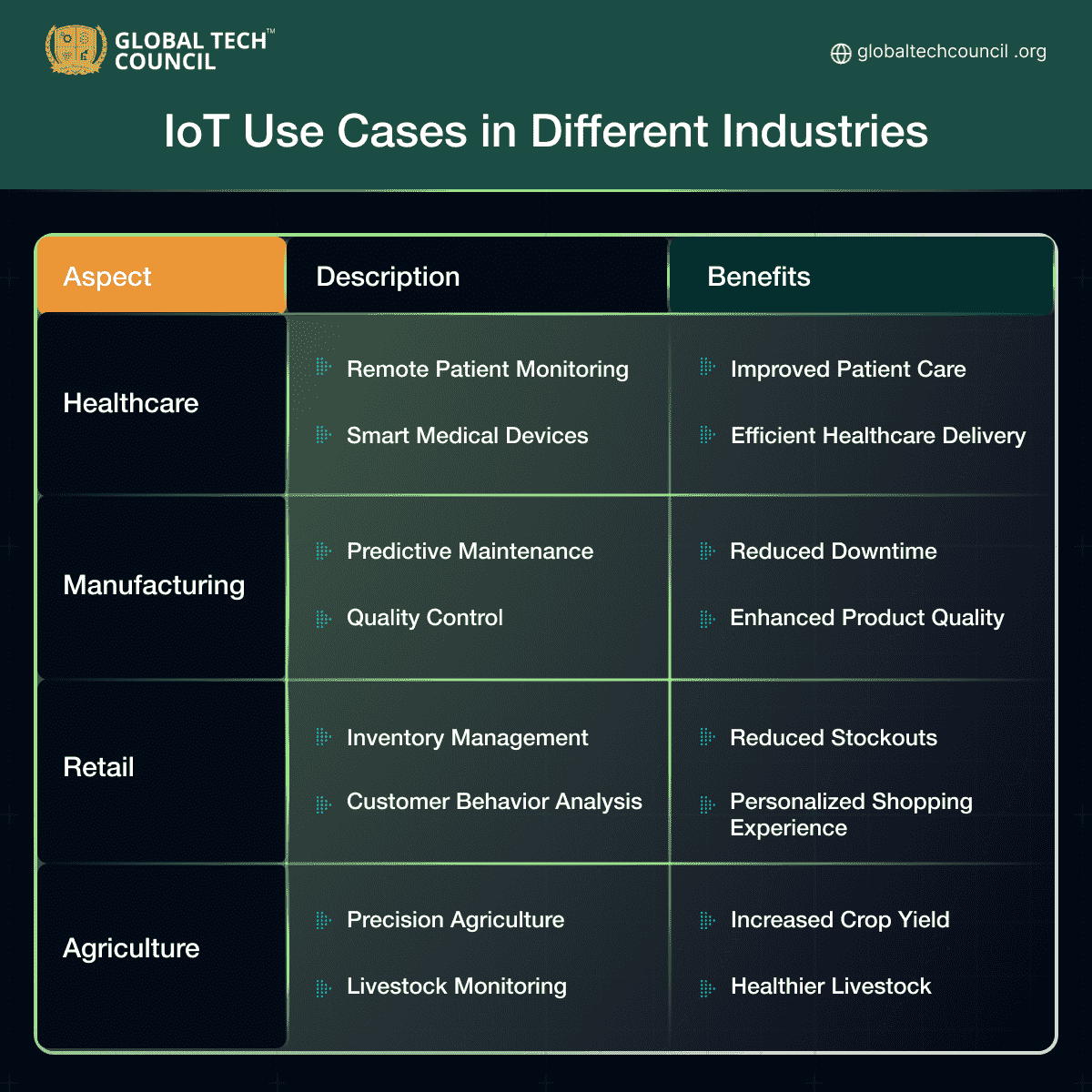
- Use cases of IoT in different industries include remote patient monitoring in healthcare, predictive maintenance in manufacturing, inventory management in retail, and precision agriculture in agriculture.
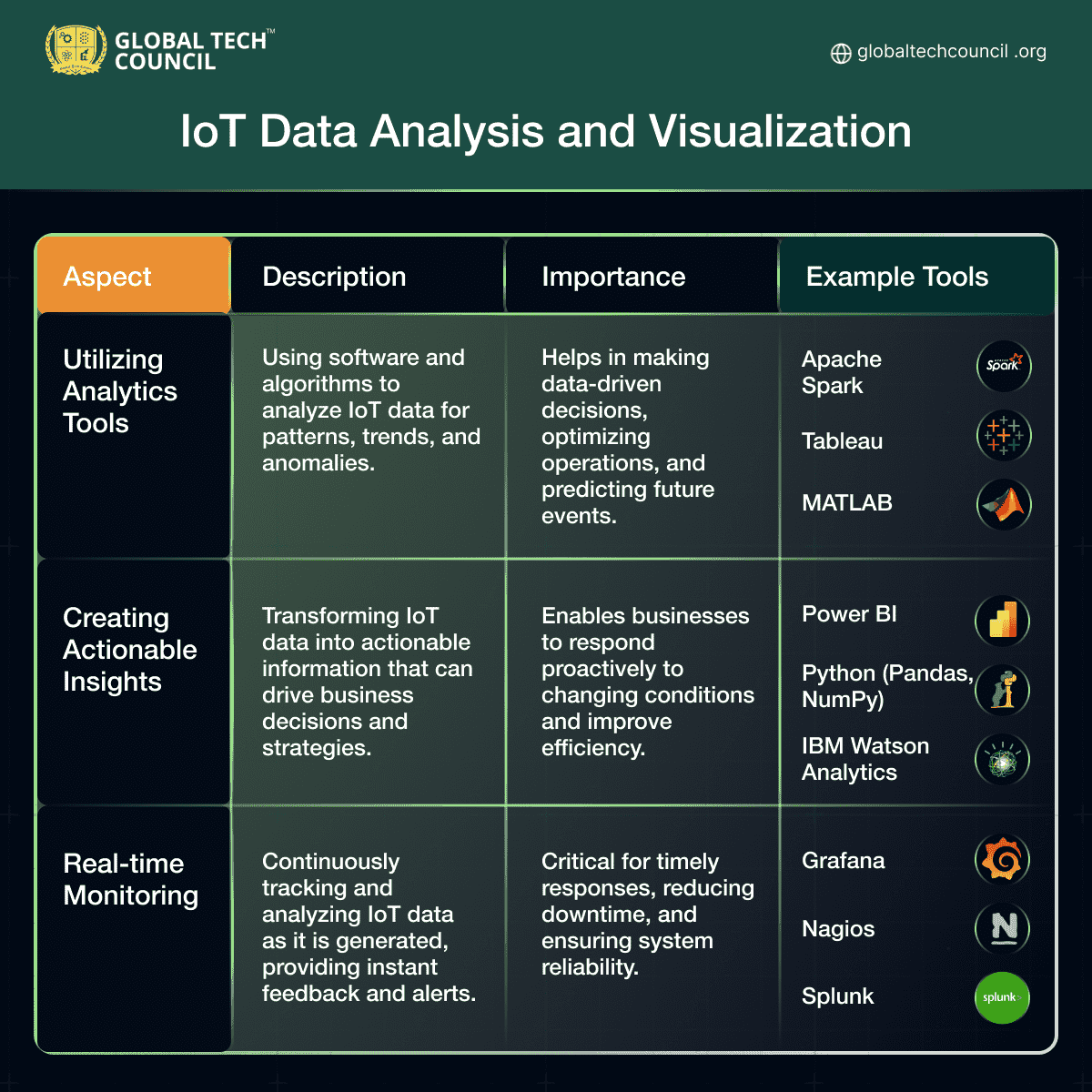
- IoT data analysis involves using analytics tools for pattern recognition, creating actionable insights, and real-time monitoring with tools like Apache Spark, Tableau, Power BI, and Grafana.
- Measuring IoT ROI involves identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), evaluating cost savings, and assessing the broader business impact beyond just cost reduction, emphasizing the transformative nature of IoT in the business landscape.
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of interconnected devices, collecting and sharing data. IoT devices include sensors, cameras, and other objects that can communicate over the internet. These devices can monitor, control, and exchange data to improve efficiency and make informed decisions. IoT technology enables businesses to connect, analyze, and optimize processes for greater productivity.
IoT has become crucial for modern businesses to stay competitive and meet evolving consumer demands. It provides real-time data, enhancing decision-making, operational efficiency, and customer experiences. IoT can transform industries like manufacturing, healthcare, logistics, and agriculture with automation and insights. Businesses utilizing IoT gain a competitive edge, cost savings, and improved resource management.
This guide aims to demystify IoT, helping businesses harness its potential effectively. Learn how IoT can enhance processes, drive innovation, and create new revenue streams. Discover practical strategies and insights to implement IoT solutions tailored to your business needs. Unlock the power of IoT and stay ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of modern business.
Also Read: TOP IOT BENEFITS AND APPLICATIONS IN THE CONSTRUCTION INDUSTRY
Understanding IoT Technology
IoT Components and Ecosystem
IoT comprises a network of interconnected devices, sensors, and systems that collect and exchange data. These are the entry points of data, such as sensors and smart devices, collecting real-time information. Collected data is processed and analyzed to extract meaningful insights for informed decision-making. Cloud platforms store and manage data, offering scalability and accessibility to users. IoT leverages advanced analytics and AI to provide valuable predictions and recommendations.
IoT Connectivity Protocols
IoT employs various communication methods, including wired (Ethernet) and wireless (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, etc.). IoT devices can connect via cellular networks, offering widespread coverage. Ideal for low-energy devices, LPWANs ensure long-range connectivity. Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) and Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) enhance IoT communication. IoT security is vital, with protocols like SSL/TLS and OAuth safeguarding data. Choosing the right protocol depends on the specific requirements of the IoT application.
IoT Devices and Sensors
IoT utilizes various sensors like temperature, humidity, motion, and more for data collection. IoT revolutionizes industries with sensors monitoring equipment health and performance. Health and fitness wearables provide users with personalized data and feedback. Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tags enable real-time tracking of assets and inventory. Embedded sensors are integral to IoT systems, ensuring seamless data flow.
Also Read: IOT IN AGRICULTURE: ALL YOU NEED TO KNOW
Benefits of Implementing IoT in Business
IoT Use Cases in Different Industries
IoT Data Analysis and Visualization
Measuring IoT ROI
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Measuring IoT’s return on investment starts with identifying the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). These indicators provide valuable insights into your IoT initiatives’ effectiveness. For example, you can track KPIs like device uptime, data accuracy, or response time to gauge performance.
- KPIs can also encompass customer-centric metrics. Customer satisfaction scores, user engagement, and service quality improvements are all relevant. Remember, the right KPIs should align with your specific business goals and objectives.
Evaluating Cost Savings
- IoT can generate significant cost savings for your business. Start by considering the efficiency gains IoT offers. Reduced energy consumption, optimized maintenance schedules, and streamlined operations can lead to substantial savings.
- Maintenance costs can be a major area where IoT shines. Predictive maintenance, enabled by IoT, can help you identify potential issues before they become costly problems.
Assessing Business Impact
- The true ROI of IoT goes beyond cost savings; it also extends to the broader business impact. How does IoT enhance your competitive edge? Does it open new revenue streams? These questions are essential.
- IoT can transform your business model. For instance, if you’re in the retail industry, IoT-driven inventory management can reduce stockouts, boost sales, and enhance customer satisfaction. This kind of positive impact is a key factor in ROI assessment.
- To evaluate the business impact, monitor metrics such as market share growth, revenue growth, and customer acquisition rates.
Conclusion
Integrating IoT into your business operations offers a multitude of advantages. IoT streamlines processes, improving efficiency, and reducing operational costs. Furthermore, it enhances data-driven decision-making, leading to informed and strategic choices. IoT provides real-time insights, enabling businesses to stay competitive in rapidly changing markets. The ability to monitor and control devices remotely ensures enhanced asset management and maintenance.
IoT is not just a technological trend; it’s a fundamental shift in the business landscape. As you consider the advantages mentioned, keep in mind that your competitors are likely already reaping the benefits of IoT. By integrating IoT solutions into your business processes, you are positioning yourself to thrive in an increasingly data-driven world.
So, if you haven’t already, it’s time to take action and integrate IoT into your business. Begin by assessing your specific needs and goals, and then find the right IoT solutions. Collaborate with experts and invest in the necessary infrastructure to make IoT work for you. The future belongs to businesses that adapt and innovate, and IoT is the key to that future. Don’t wait – start your IoT journey today and reap the rewards it brings to your business.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is IoT, and how does it benefit businesses?
- IoT, or the Internet of Things, is a network of interconnected devices that collect and share data over the internet.
- Businesses benefit by using IoT devices like sensors and cameras to monitor, control, and exchange data, leading to improved efficiency, informed decision-making, and a competitive edge.
- How does IoT data analysis work, and what tools are commonly used?
- IoT data analysis involves using software and algorithms to analyze real-time data for patterns, trends, and anomalies.
- Commonly used tools include Apache Spark, Tableau, Power BI, Python (Pandas, NumPy), IBM Watson Analytics, Grafana, Nagios, and Splunk.
- What are some examples of IoT use cases in different industries?
- IoT is applied across industries with examples like remote patient monitoring in healthcare, predictive maintenance in manufacturing, inventory management in retail, and precision agriculture in agriculture.
- These use cases lead to improved patient care, reduced downtime, personalized shopping experiences, and increased crop yield.
- How can businesses measure the return on investment (ROI) of implementing IoT?
- Businesses can measure IoT ROI by identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) such as device uptime, data accuracy, and response time.
- Evaluating cost savings, especially in areas like energy consumption and maintenance costs enabled by predictive maintenance, is essential.
- Additionally, assessing the broader business impact, including market share growth and revenue growth, provides a comprehensive view of the ROI of IoT implementation.